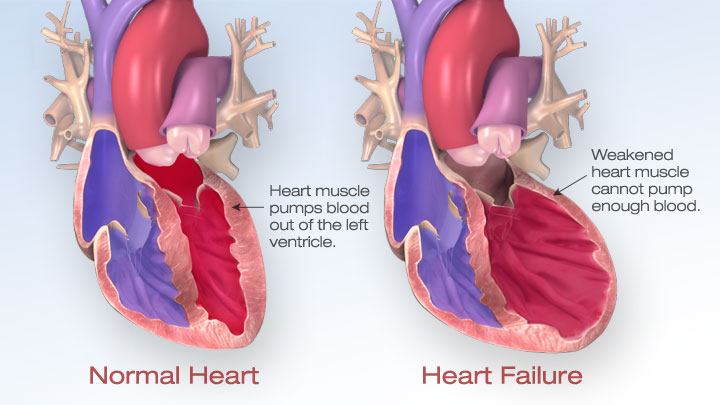
Heart failure does not mean the heart has stopped working; it means that the heart works less efficiently than normal because of various causes. Depending upon types of onset, it can be acute or chronic. It developing sudden in the patient with Myocardial Infarction is acute & Valvular heart disease is a chronic, with gradual deterioration of heart function. It is the leading cause of hospitalization & life-threatening at older age.
Heart failure effects on Cardiac output (body blood circulation), due to various possible causes, blood moves through the heart to the body at a slower rate which causes an increase in heart pressure. As a result, the heart cannot pump enough oxygen and nutrients to meet the body’s needs. Congestive heart failure (CHF) specifically refers to the stage in which fluid builds up around the heart and causes it to pump inefficiently, also resulting fluid builds up in the arms, legs, feet, ankles, abdomen, lungs, other organs & the body becomes congested.
What are the Causes of Heart Failure (HF)?
- Ventricular outflow obstruction: A) Left Ventricular outflow obstruction(Pressure overload): Hypertension & Aortic Stenosis, B) Right Ventricular outflow obstruction: Pulmonary Hypertension & Pulmonary Stenosis,
- Ventricular Inflow Obstruction: Mitral Stenosis(left side inflow obstruction), Tricuspid Stenosis(right side inflow obstruction), Endomyocardial fibrosis,
- Ventricular volume overload: Atrial or Ventricular septal defect, Mital or Aortic regurgitation, Mitral valve prolapse etc.
- Depressed Ventricular contractility: A) Coronary artery disease: Coronary artery disease (CAD), a disease of the arteries that supply blood and oxygen to the heart, causes decreased blood flow to the heart muscle. If the arteries become blocked or severely narrowed, the heart becomes starved for oxygen and nutrients. A heart attack occurs when a coronary artery becomes suddenly blocked, stopping the flow of blood to the heart muscle. A heart attack damages the heart muscle, resulting in a scarred area that does not function properly. B) Cardiomyopathy: Damage to the heart muscle from causes other than artery or blood flow problems, such as from infections or alcohol or drug abuse, C) Myocarditis, D) Myocardial ischemia etc.
- Conditions that overwork the heart & other: Conditions including high blood pressure, massive blood loss, thyroid disease, kidney disease, heart defects present at birth may cause heart failure. In addition, it can occur when several diseases or conditions are present at once.
Precipitating & Aggravating causes of Heart Failure(HF):
- Infection
- Pulmonary embolism
- Anaemia, pregnancy, thyrotoxicosis
- Cardiac arrthymias
- Myocarditis
- Hypertension
- Fluid retention due to high salt intake
- Drugs negative effect (beta blockers, corticosteroid, NSAIDs etc.)
- Physical & emotional stress etc.
Sign & symptoms of Heart Failure can be:
- Due to low cardiac output Fatigue, low blood pressure, cold extremities, poor effort tolerance
- Dyspnoea, Orthopnoea, Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea
- Cardiac asthma
- Acute pulmonary & cardiac oedema
- Diminished pulse pressure
- Cough & expectoration
- Anoxia, Nausea & Vomiting
- Jaundice
What are the common types of Congestive heart failure (CHF):
Left-sided CHF is the most common type of CHF. It occurs when your left ventricle doesn’t properly pump blood out to your body. This area pumps oxygen-rich blood to the rest of your body. As the condition progresses, fluid can build up in your lungs, which makes breathing difficult.
Risk factors of CHF:
- Hypertension: When your blood pressure is higher than normal, it may lead to cardiac problems as well as CHF. So maintain your proper blood pressure.
- Coronary artery disease & Arteriosclerosis: Cholesterol and other types of fatty substances can plaque in the blood vessels & block the coronary arteries, which are the small arteries that supply blood to the heart. Arteriosclerosis causes the arteries to become narrow, restrict the blood flow and it can lead to damage in of the arteries.
- Heart valve anomalies: Heart valves regulate blood flow through your heart by opening and closing to let blood in and out of the chambers. Valves that don’t open and close correctly may force your ventricles to work harder to pump blood.
- Bad habits: Tobacco, alcohol & illegal drugs
- Other conditions: These include diabetes, obesity and thyroid disease etc.
How to Prevent CHF:
- There are several things you can do to lower your risk of HF or may improve your health.
- Avoid or quit smoking- Click & Know more about this
- Maintain a well-balanced diet: Take healthy diet; eat vegetables, fruits, and whole grains. Dairy products should be low-fat or fat-free. Avoid more salt (sodium), added sugars, solid fats, and refined grains.
- Exercise regularly, Walking, bicycling, and swimming are good forms of exercise.
- Moderate & Balanced lifestyle
- Maintain proper body weight.
- If you are suffering with high blood pressure, heart disease, or diabetes, take proper medicine & control it. Visit your doctor regularly to monitor your condition and report.
What are the symptoms of CHF?
In most of the cases the early stages of CHF, patients won’t likely to be notice. If the condition progresses, patient will experience gradual changes in his/her body.
- Fatigue
- Swelling in your ankles, feet, and legs
- Weight gain
- Irregular heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing & cough that develops from congested lungs
- Chest pain that radiates through the upper body
- Skin that appears blue, which is due to lack of oxygen in your lungs
- Fainting etc.
How is Congestive Heart failure (CHF) diagnosed?
The proper check-up can be done a heart specialist, or cardiologist, he/she will perform a physical exam. To confirm an initial diagnosis, your cardiologist might order certain diagnostic tests to examine your heart’s valves, blood vessels, and chambers.
- Electrocardiogram(ECG or EKG)
- Echocardiogram
- MRI
- Blood tests
Cardiac catheterization etc.
Treatment of CHF?
The doctor can do different treatment; treatment plan will be depending upon your condition, don’t neglect it take proper doctor advice. Know about different treatment options for CHF.
- Medicines: Congestive heart failure drugs which including ACE inhibitors, diuretics, NSAIDs, Beta-Blockers etc.
- Surgeries: If medications aren’t effective on their own, more invasive procedures may be required. Angioplasty, a procedure to open up blocked arteries, is one option. Your cardiologist may also consider heart valve repair surgery to help your valves open and close properly.


0 Comments